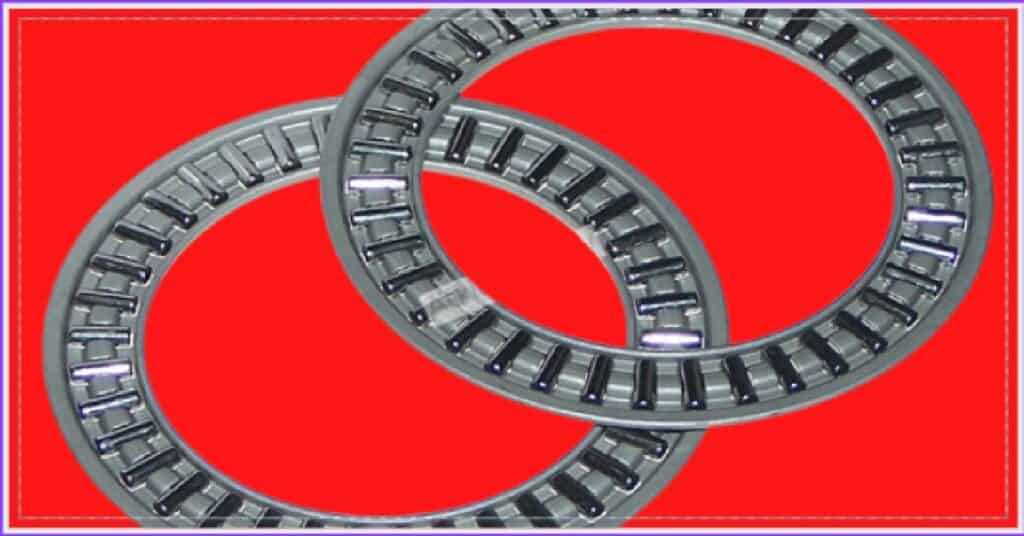
You can find Thrust washers in nearly every appliance, machine, transportation, power tool, and already moving parts, axles, bolts, pins, bearings, recreational equipment, components, and rotating parts.
In its simplest form, a thrust washer is a washer-shaped long-wear bearing that transmits and resolves axial forces in a rotating mechanism to maintain the components aligned along the shaft.
So long as speeds are kept moderate, thrust washers are a more affordable alternative to rolling bearing bearings.
Why Thrust Washer Was Invented
For the invention of the wheel, the need for thrust washers appears almost ancient in antiquity.
These sturdy washer-shaped flat bearings are used to prevent lateral movement of the wheel on the shaft when the bearing moves around a radially loaded bearing such as a bushing or roller bearing without specially provided bearings for axial or thrust loads.
Typical lateral or axial loads are encountered whenever a corner is turned and the vehicle is pushed toward the outside of the buckling bend.
Other applications of our ancestors would be grain mills, water wheels, turntables, and rotary drills, whatever the primary motion may have radial and axial forces to cope with.
Of course, the propeller shafts on each propeller drive vessel from largest to smallest vessel must have thrust bearings to resolve the linear and axial thrust of the rotating propeller, either forward or aft.
What Materials Is Thrust Washer Made Of
Thrust washers are made from many different materials and selected for the best performance, maintenance, and price combination.
Most hardened steel shafting applications will use grease-type washers, a very porous bronze material that can hold over 30% oil volume. Therefore, Whetstone is self-lubricating.
Sometimes sleeve bearings around the shaft incorporate their thrust washers; these sleeves are called flanged sleeve bearings.
Different Ways To Use Thrust Washer
One of them on each end of the motor shaft will account for all radial and axial forces presented by the motor.
Another variation on standard thrust washers is to use several series in series whenever the VMAX or maximum speed in RPM exceeds the normal specification for sliding (non-rolling) bearings, such as a single thrust washer.
A damping function is added to the thrust washer’s ability to absorb rotational vibration and act as a dynamic brake when a high-viscosity fluid such as silicone or heavy oil is applied to the chip former.
Each appliance motor has at least one thrust washer to control axial displacement, also known as the end game.
The propeller shafts on most inboard and outboard boats use at least one thrust washer to transfer the axial thrust of the rotating propeller to forward or aft motion.
Various obstacles use thrust washers as weight bearings and unstable motion dampers.
What Are The Shortcoming Of Thrust Washers
Thrust washers dissipate some of the rotational energy in the system as friction due to all sliding and not rolling bearings.
Therefore, they are always less efficient than ball or roller-bearing thrust-bearing systems.
Function Of Thrust Washer
A thrust washer is a flat bearing that sandwiches between a rotating and stationary component. It keeps the rotating component in place by giving it something to brush up against if it starts to move sideways.
Thrust Washer Failure Symptoms
How will you recognize a defective thrust bearing? Below will be explain
Thrust bearings are parts that usually last a long time and easily do their job for more than 100,000 kilometers.
When the part’s life is nearing its end, you will notice this mainly in the unusual noises. This way, the rattling, whistling, or squeaking can be heard quietly at first and later more and more clearly.
When the clutch pedal is depressed, the sound frequently changes. In severe circumstances, gear selection is affected because the clutch can no longer be fully separated if the release bearing or lever is destroyed.
Why Does The Thrust Bearing Fail?
The most common cause of thrust-bearing failure is fatigue. The grease between the parts loses its lubricating effect over time, and excessive friction is created.
The problem then gets bigger because of the non-circular run. In addition to this unavoidable wear and tear, driving style can also lead to premature failure of the release bearing.
Especially at traffic lights or level crossings, you should always switch to idle to protect the release bearing rather than interrupting the power supply through the clutch.
The release bearing and release fork can be damaged by the permanent load on the disc springs and cause premature failure.
In the worst case, the release lever can even break. With unguided clutches, there is also a risk that the release bearing on the gear shaft will rub.
The wear can then lead to further consequential damage in the transmission. Long car downtimes are also unfavorable for the release bearing.
There is a risk of rust forming between the gear shaft and the bearing.
How To Replacing Thrust Bearing
Checking and replacing the release bearing is not a job for the home garage and should only be carried out in a specialized workshop.
The drive shafts detached from the gearbox and the gearbox from the engine. Removing the gearbox alone can take several hours, and due to the heavyweight, there is also a significant risk of injury if suitable tools such as a lifting platform and jack are not present.
First, the wheels are disassembled, then the drive shafts or cardan shafts are detached from the gearbox, and possibly interfering parts such as the generator or starter are removed. Finally, the gearbox bearings are unscrewed.
The gearbox can then be removed from the engine compartment using a gearbox jack. This big job is an excellent opportunity to check all other parts related to the clutch and transmission and replace them if necessary.
This includes the bearings, seals, clutch disc, and flywheel. The old thrust bearing is removed with the thrust fork and replaced with new parts. The bearings are thoroughly cleaned and lubricated with long-lasting grease.
A minimum of two (better three) persons is required for the retrofitting, as the gearbox must be put back in place. Of course, you use new screws and tighten them with the correct torque.
WHAT IS The Cost Of Replacing The Thrust Bearing.
A defective release bearing is always annoying because the installation is very complex. In this way, the costs are kept to a minimum.
Depending on the car, it can take several hours to get the job done and cost up to €1,000. In addition, it can be useful to replace the clutch and flywheel at the same time.
The best option is to go with well-known brands like LuK, Meyle, or SKF in order to prevent unpleasant surprises. Second-hand parts are not something we advise.
NOTE:
While installing thrust bearing, please take note of the following:
(1) Distinguish between the tight ring and the loose ring of the bearing (judging by the inner diameter of the bearing, the difference in the diameter of the bearing is O.1 ~ O.5mm).
(2) Distinguish the static parts of the mechanism (that is, the parts that do not move, mainly referring to the assembly).
(3) In any case, the loose ring of the bearing should always rest on the end face of the stationary part.
Summarize
Thrust washers are the most economical and easiest to apply of all thrust bearing replacements. Like all mechanical systems, they work best when kept clean and lubricated.